Certification testing and grants are making V2V and V2I connection protocols ready for deployment. The US Department of Transportation and Federal Highway Administration are working with partners to create standards and testing procedures for connected vehicles.
Certification testing and grants are making V2V and V2I connection protocols ready for deployment. The US Department of Transportation and Federal Highway Administration are working with partners to create standards and testing procedures for connected vehicles.
The US Department of Transportation’s (USDOT) Intelligent Transportation Systems Joint Program Office (ITS-JPO) and the Certification Steering Committee have started to work with Danlaw, 7Layers and OCS to set up and deliver the next generation of certification services in support of the Connected Vehicle Pilot Deployment Program and other near-term projects
The three companies will work with the USDOT to define the scope of certification activates, test procedures t and test equipment. Related communities will be consulted at each step of the process. Once the procedures and equipment lists are determined, the companies will set up facilities to operate the tests.
Telematics engineering company Danlaw, Inc. announced that it was awarded a grant by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) to develop the Next Stage Certification Environment for connected vehicle technology for (DSRC) Dedicated Short Range Communication and standard, IEEE 802.11p.
DSRC is a range dedicated for cars only and has a great potential. In fact, DSRC is being used to make highways with wireless electric vehicle charging built-in.
Danlaw will develope standardized certification techniques, tools and the associated test environment for certification of the communication protocol, vehicle interface and environmental interactions associated with DSRC based connected devices.
Certification testing is important to ensure that future DSRC based devices communicate accurately and with high reliability for the greatest safety.
Danlaw noted that as it develops the next generation DSRC certification environment, it looks forward to working with other DSRC stakeholders, device and component manufacturers, USDOT and Test Bed Operators to develop and finalize device specifications, test procedures, test suites, and supporting Plug Fests.
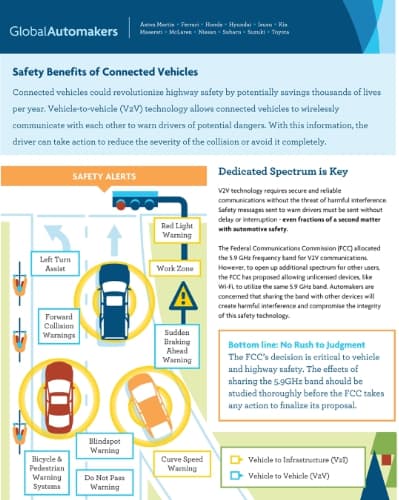
DSRC communications take place over a dedicated 75 MHz spectrum band around 5.9 GHz, allocated by the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for vehicle safety applications. DSRC is preferred over Wi-Fi because the proliferation of Wi-Fi hand-held and hands-free devices that occupy the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, along with the projected increase in Wi-Fi hot spots and wireless mesh extensions, could cause intolerable and uncontrollable levels of interference that could hamper the reliability and effectiveness of active safety applications.
The DOT has not stated when it will require the deployment of DSRC in vehicles.
Danlaw has offices in the USA, UK, India and China. Danlaw’s specialty areas include telematics, infotainment, vehicle network communications, embedded systems development, testing and manufacturing. Their customers include automotive insurance and fleet companies, automotive OEMs and suppliers.
A video from DOT Connected Vehicle: The Future of Transportation explains an overview of the connected car future.